 â
âUnmet Need: Enabling independent bowel management for individuals with limited dexterity due to neurodegenerative disease or spinal injury
Millions of people worldwide live with spinal cord injuries or neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In these populations, neurogenic bowel, bowel dysfunction, and incontinence are common and have a great impact on not only physical health but also functional independence. Thus, independent and efficient bowel management is crucial to maintaining health by minimizing incontinence while maximizing autonomy, dignity, and quality of life for patients and caregivers.
The Technology: A Prototype Delivery Mechanism to Improve Bowel Function and Continence
To address this need, WSU inventors have collaborated with spinal cord injury specialist Dr. Glen House to develop an innovative medical device that allows patients with limited mobility to self-administer bowel stimulants as part of their bowel program. The device is designed to effectively apply small volumes of bowel stimulants directly to bowel wall, improving bowel function and continence. The product is designed with safe, easy, and controlled delivery in mind, particularly for those with limited mobility in the upper extremity.
The prototype facilitates use from an upright, seated position and consists of an inserter, arm, and lever actuator. The inserter size is optimized to efficiently deliver the bowel stimulating drug while maximizing safety and comfort. The long arm and large lever actuator permits controlled delivery of a liquid stimulant to the bowel wall and allows delivery by pressing with a hand, elbow, or shoulder. This innovation targets the improvement of bowel function and continence while enhancing independence.
Applications:
Advantages:
Patent Information:
Provisional patent has been filed.
PRODUCT OPPORTUNITIES
PRODUCT OPPORTUNITIES
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
TECHNOLOGY DESCRIPTION
ABOUT THE INVENTOR
AVAILABILITY:
Available for Licensing and/or Sponsored Research
DOCKET:
UMA 18-067
PATENT STATUS:
NON-CONFIDENTIAL INVENTION DISCLOSURE
LEAD INVENTOR:
CONTACT:
Biosensors are well known and used in a number of applications. These devices operate by altering the current/voltage response of the FET when a target analyte binds to a capture agent on the FET surface. However, conventional biosensors current biosensors lack the ability to detect the presence of extremely low concentrations of target analytes. One class of biosensors uses an odorant receptor membrane protein to detect the presence of a target analyte. Here, an e-nose sensor is disclosed that utilizes odorant receptors a source electrode, a drain electrode, and a semiconducting region that connects or electrically couples the source and drain electrodes. A lipid bilayer is disposed on or adjacent to the semiconducting region and includes an odorant receptor protein that is coupled or fused to an ion channel protein. The semiconducting region changes its electrical conductance in response to the presence of ions adjacent to the semiconducting region that enter in response to binding of a target molecule (e.g., odorant) to the odorant receptor protein. The sensor is able to detect the binding of a single target molecule. Because this sensor is electronic it could be integrated in the future into a massively parallel e-nose system with signal recognition based on hundreds of different odorant receptor sensors integrated onto one chip. The sensor may be used to detect the presence of target molecules present in air or it may be used to detect target molecules present in a fluid (e.g., a biological fluid or environmental fluid sample).
This user-friendly test kit enhances the detection of glyphosate-based herbicides in water through advanced analytical techniques. Utilizing pre-column derivatization coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), the kit simplifies the derivatization and pretreatment process for on-site sample preservation. Its design aims to make glyphosate detection more accessible and accurate even at trace levels, ensuring environmental monitoring and water safety measures can be efficiently implemented.
â
 â
â
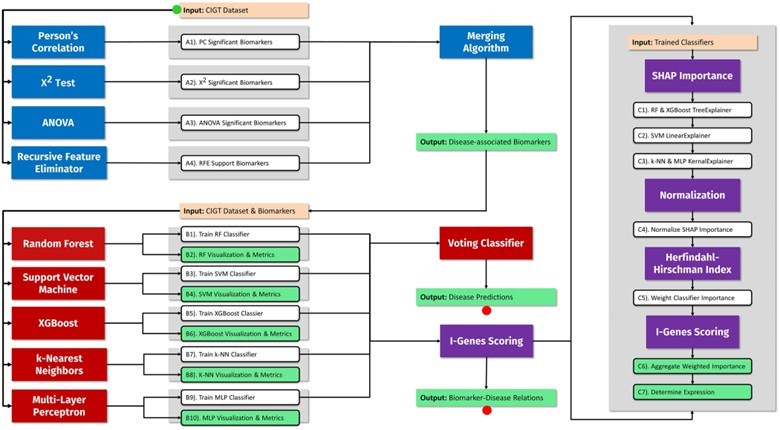
A pipeline combining classical statistics and machine learning algorithms is used to identify disease-associated biomarkers and predict disease risk
Invention Summary:
Gene Expression Analysis and Genomeâwide association studies provide an unprecedented understanding of the genetic basis of human disease by uncovering millions of loci associated with various complex disease phenotypes. However, these are unable to completely map biomarkers and predict disease with high accuracy. The key limitation is our lack of technology to analyze the complete genome or transcriptome of patients to identify all the genetic components of complex traits.
To address this, researchers at Rutgers University have developed a software pipeline to help predict diseases in individuals by combining conventional statistical methods with cutting-edge machine learning algorithms to measure the significance of genomic biomarkers. The pipeline can intake data including patient demographics, genomic and transcriptomic data to produce personalized patient predictions and visual representations of the biomarkers significant to disease prediction.
Market Applications:
Application integrated with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems
Precision Medicine, personalized genetic insights, sequencing as a service companies
Research institutions / universities
Diagnostic Lab Testing
Pharmaceutical companies
Advantages:
Comprehensive biomarker discovery
Two-in-one functionality: identifies disease-associated biomarkers and predicts patient diagnoses
Easy to use interface, allowing those without prior AI background to use the platform
Does not require access to high-performing computers
Market for application of AI to precision medicine is ~ USD 1.3 billion in 2022
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Patent pending. Software available for licensing and/or research collaboration.â¯For any business development and other collaborative partnerships contact marketingbd@research.rutgers.edu.
Publication available: https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/39/12/btad755/7473370
â
Improvement to supercapitors is necessary to match new technologies
Supercapacitors are a type of electrochemical energy storage system that are often used when rapid charge/discharge cycles (burst power) are desired in comparison to) long-term energy storage. As modern technology grows increasingly complex, energy requirements have grown, and continuous research is being conducted to improve supercapacitors.
Implants can cause hot spots and burns during MRI scans
Patients undergoing MRI scans sometimes experience hot spots and burns, mostly due to external or implanted metallic objects such as pacemakers or orthopedic implants. This is caused by radio frequency (RF)-induced heating as the current distribution over the patientâs body can cause the temperature to rise. This cannot be avoided because MR systems work by imaging phantoms to determine specific absorption rates (SAR) or temperature rise in the patient.
Therefore, there is a need for a small sensor that can provide information about the local RF field during imaging procedures. Furthermore, all medical implants need to be evaluated for SAR impact during the development phase.
Gas sensors play a critical role in everyday life by detecting specific gases in the environment for diverse applications, including industrial safety and exposure monitoring. Portable and cheap gas sensors can be used to provide real-time monitoring of targeted gases, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Chemoresistors are a type of VOC sensor that works by changing their electrical resistance in the presence of the VOC. These chemoresistors are small, cheap, and easy to use, making them ideal for fieldwork.
Current on-chip filters are too big and non scalable
Developed for applications exceeding 30 GHz, this "combline" electromagnetic filter technology leverages the phase-change properties of Vanadium Dioxide (VO2) to adjust its passband frequency range dynamically. Heating VO2 creates a high-performance ground connection, reducing the electrical length of coupled transmission lines and thus shifting the passband to a higher frequency.
Spot tasks are limited by complex needs to render features
The usage of smartphones and mobile devices has continuously grown over the last decade, and with about 51% of enterprise workers using mandated apps on their phones for business-related purposes, this has led to an increase in opportunities where spot tasks have become applicable. The enabling of spot tasks can often be limited by the constraint of needing to render all features of original applications onto a small screen and the need for complex image recognition or user-defined UI subset for smartphone rendering.